A team led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a novel, integrated approach to track energy-transporting ions within an ultra-thin material, which could unlock its energy storage potential leading toward faster charging, longer-lasting devices.
Scientists have for a decade studied the energy-storing possibilities of an emerging class of two-dimensional materials – those constructed in layers that are only a few atoms thick – called MXenes, pronounced “max-eens.”
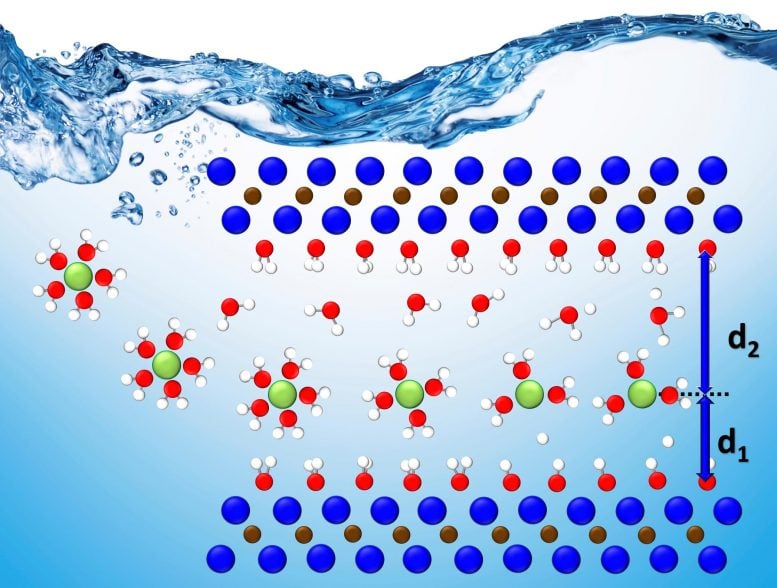
The ORNL-led team integrated theoretical data from computational modeling of experimental data to pinpoint potential locations of a variety of charged ions in titanium carbide, the most studied MXene phase. Through this holistic approach, they could track and analyze the ions’ motion and behavior from the single atom to the device scale.
“By comparing all the methods we employed, we were able to form links between theory and different types of materials characterization, ranging from very simple to very complex over a wide range of length and time scales,” said Nina Balke, ORNL co-author of the published study that was conducted within the Fluid Interface Reactions, Structures, and Transport, or FIRST, Center. FIRST is a DOE-funded Energy Frontier Research Center located at ORNL.
“We pulled all those links together to understand how ion storage works in layered MXene electrodes,” she added. The study’s results allowed the team to predict the material’s capacitance, or its ability to store energy. “And, in the end, after much discussion, we were able to unify all these techniques into one cohesive picture, which was really cool.”
Layered materials can enhance energy stored and power delivered because the gaps between the layers allow charged particles, or ions, to move freely and quickly. However, ions can be difficult to detect and characterize, especially in a confined environment with multiple processes at play. A better understanding of these processes can advance the energy storage potential of lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors.
As a FIRST center project, the team focused on the development of supercapacitors – devices that charge quickly for short-term, high-power energy needs. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy capacity and provide electrical power longer, but the rates of discharge, and therefore their power levels, are lower.
MXenes have the potential to bridge the benefits of these two concepts, Balke said, which is the overarching goal of fast-charging devices with greater, more efficient energy storage capacity. This would benefit a range of applications from electronics to electric vehicle batteries.
Using computational modeling, the team simulated the conditions of five different charged ions within the layers confined in an aqueous solution, or “water shell.” The theoretical model is simple, but combined with experimental data, it created a baseline that provided evidence of where the ions within the MXene layers went and how they behaved in a complex environment.
“One surprising outcome was we could see, within the simulation limits, different behavior for the different ions,” said ORNL theorist and co-author Paul Kent.
The team hopes their integrated approach can guide scientists toward future MXene studies. “What we developed is a joint model. If we have a little bit of data from an experiment using a certain MXene, and if we knew the capacitance for one ion, we can predict it for the other ones, which is something that we weren’t able to do before,” Kent said.
“Eventually, we’ll be able to trace those behaviors to more real-world, observable changes in the material’s properties,” he added.
The paper, titled “Tracking ion intercalation into layered Ti3C2 MXene films across length scales,” was co-authored by Qiang Gao, formerly of ORNL; Weiwei Sun of Vanderbilt University and formerly of ORNL; Arthur P. Baddorf, Nina Balke, Jingsong Huang, Stephen Jesse, Paul Kent and Wan-Yu Tsai of ORNL; Nadine Kabengi and Poorandokht Ilani-Kashkouli of Georgia State University; Alexander Tselev of the University of Aveiro, Portugal; Michael Naguib of Tulane University; and Yury Gogotsi of Drexel University.
Reference: “Tracking ion intercalation into layered Ti3C2 MXene films across length scales” by Qiang Gao, Weiwei Sun, Poorandokht Ilani-Kashkouli, Alexander Tselev, Paul R. C. Kent, Nadine Kabengi, Michael Naguib, Mohamed Alhabeb, Wan-Yu Tsai, Arthur P. Baddorf, Jingsong Huang, Stephen Jesse, Yury Gogotsig and Nina Balke, 8 July 2020, Energy and Environmental Science.
DOI: 10.1039/D0EE01580F
The research was sponsored by DOE’s Office of Science, though the FIRST EFRC, and used resources at the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences at ORNL and the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, both Office of Science user facilities.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the DOE Office of Science. The single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, the Office of Science is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.